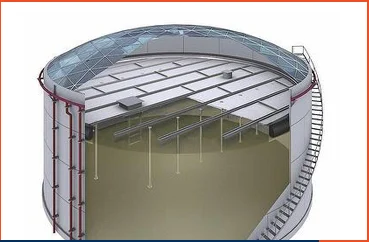
As an engineer in the petroleum industry, you are likely familiar with the necessity of proper storage tank design for hazardous materials. Internal floating roofs are an ideal solution for many toxic or volatile liquids, but their construction can be quite complex. This article provides an overview of the key components in an aluminum internal floating roof system to help you better understand their function and importance. With strict environmental regulations and safety standards to uphold, ensuring the integrity of any storage tank is critical. An aluminum internal floating roof uses a durable, lightweight design to prevent emissions, reduce fire risk, and increase operational efficiency. By examining each part that comprises these advanced roofing systems, you will gain valuable insights into how they operate and how to specify the proper configuration for your facility’s needs.
Primary Components of Aluminum IFR Design
The key components of an aluminum internal floating roof comprise the roof itself, seals, liquid-mounted pontoons or double deck roofs, and fixed roof support legs.
The aluminum roof panels form the floating roof barrier and are joined together with sealant and bolts to create a complete cover over the stored liquid. High-quality aluminum materials prevent corrosion and ensure the structural integrity of the roof. Multiple roof drains allow rainwater to flow off the roof into the stored liquid.
Rim seals, pipe seals and leg seals prevent vapor emissions at the edges and penetrations of the floating roof. Rim seals attach around the circumference of the roof to seal the gap between the roof and tank wall. Pipe seals fit around any pipes entering the tank. Leg seals attach to the support legs securing them to the tank floor.
Pontoons or double deck roofs are chambers mounted below the floating roof that are filled with a liquid, like water, to help support and float the aluminum roof panels. The buoyancy provided by the pontoons counterbalances the weight of the roof and any rainwater, allowing the roof to float directly on the stored liquid.
With high-quality components like aluminum roof panels, a variety of seals, pontoons for floatation and support legs for stability, an internal floating roof forms an effective barrier for controlling vapor loss and maintaining liquid integrity. Proper specification and installation of all components is critical for optimal performance and a long service life.
Secondary Components That Support IFR Functionality
The secondary components of an aluminum internal floating roof (IFR) work together to support the primary pontoon and deck structure while also facilitating essential functionality.
Vent Assemblies
Vent assemblies allow for pressure and temperature regulation within the tank. As liquid product levels change, vents automatically open and close to balance pressure. Vents are position around the perimeter of the IFR deck.
Leg assemblies
Leg assemblies connect the IFR deck to the tank shell. They allow the required deck height adjustment while also providing stability. Multiple adjustable legs around the deck perimeter enable leveling and centering of the deck. Legs may be properly tightened to prevent excess movement or vibration.
Deck Fittings
Deck fittings, such as access hatches, gage poles, and sample ports, provide access to the product below the floating roof. Access hatches allow entry under the deck for inspections and maintenance. Gage poles and sample ports enable product level monitoring and sampling. Deck fittings are strategically placed to not interfere with vent or leg assemblies.
Perimeter Seal
The perimeter seal attaches around the edge of the floating roof deck. It contacts and seals against the tank wall, preventing product vapors from escaping. Different seal types suit various tank geometries and product vapor pressures. Regular seal maintenance and adjustment help ensure optimal performance and compliance.
Deck Support Columns
Deck support columns provide stability for larger decks, especially during high wind conditions or liquid loading/unloading. They transfer forces from the deck to the tank floor while allowing unrestricted product flow under the deck. Proper column height is critical to prevent interference with vent or leg assemblies.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting IFR Components
Design
The design of the IFR components is critical. They must be engineered to properly distribute the weight of the roof across the stored product, remain securely in place, and prevent excess vapor loss. Common designs include:
- Pontoons: hollow structures that provide flotation. They are attached to the underside of the roof deck.
- Double-deck: an upper and lower deck with compartments in between that can be filled with a vapor control fluid like glycol.
- Full-contact: the roof deck rests directly on the stored product. It requires a vapor barrier and rim seals to contain vapors.
Material
Aluminum is a popular material for IFRs due to its lightweight, non-corrosive, and non-sparking properties. Aluminum alloys provide strength and durability. People often construct components like deck plates, pontoons, and seals out of aluminum. They can also use stainless steel, especially for hardware like bolts, nuts, and hinges.
Seals
Effective seals are essential to prevent vapor loss and maintain roof buoyancy. Common seals include:
- Rim seals: attach to the tank wall to seal the gap between the roof and wall. Made of rubber, aluminum, or stainless steel.
- Leg seals: seal around roof support legs. Made of rubber, aluminum or stainless steel.
- Deck seals: seal gaps and seams in the roof deck. Made of rubber, elastomer or aluminum.
- Hatch seals: seal access hatches and manways. Made of rubber.
Accessories
Other components like access hatches, roof legs, rolling ladders, and gaging devices facilitate operation, access, and monitoring of the IFR. Properly selected, high-quality components and accessories help ensure safe, efficient, and environmentally-friendly storage of volatile liquids in floating roof tanks. Carefully considering design, materials, seals, and accessories when choosing IFR components will result in a system well-suited to your specific needs and application.
Conclusion
By understanding how all these parts function as an integrated system, you can appreciate the ingenuity of aluminum internal floating roof storage tank design.
Proper specification, installation and maintenance of each component is key to optimizing performance and ensuring regulatory compliance. With the right design, these roofs provide an elegant solution for dangerous or polluting liquid storage applications.