As an engineer designing fluid storage systems, Selecting the Perfect Low-Profile is one of the most critical choices you will make. The seals create an essential barrier between the internal and external environments, preventing leaks and ensuring structural integrity. For many applications, a low-profile secondary seal offers an ideal solution. These seals provide a thin, space-efficient layer of protection at a lower cost than some alternatives.
However, with many options on the market, determining the perfect low-profile seal for your needs can be challenging. You must consider factors like the fluids or gasses being contained, the operating environment, installation requirements, and long-term durability needs. The wrong choice can lead to catastrophic failure, while the right choice helps enable an efficient, cost-effective design with a long service life.
This article provides an overview of the most common types of low-profile secondary seals, their properties, and recommendations for the best options based on your operating conditions. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each seal type, you can make an informed choice and select a high-quality, long-lasting solution for your storage system. The result is a safer, more sustainable product for you and your customers.
What Is a Low-Profile Secondary Seal?
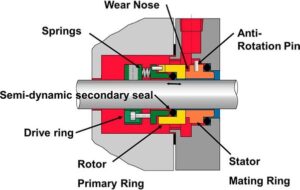
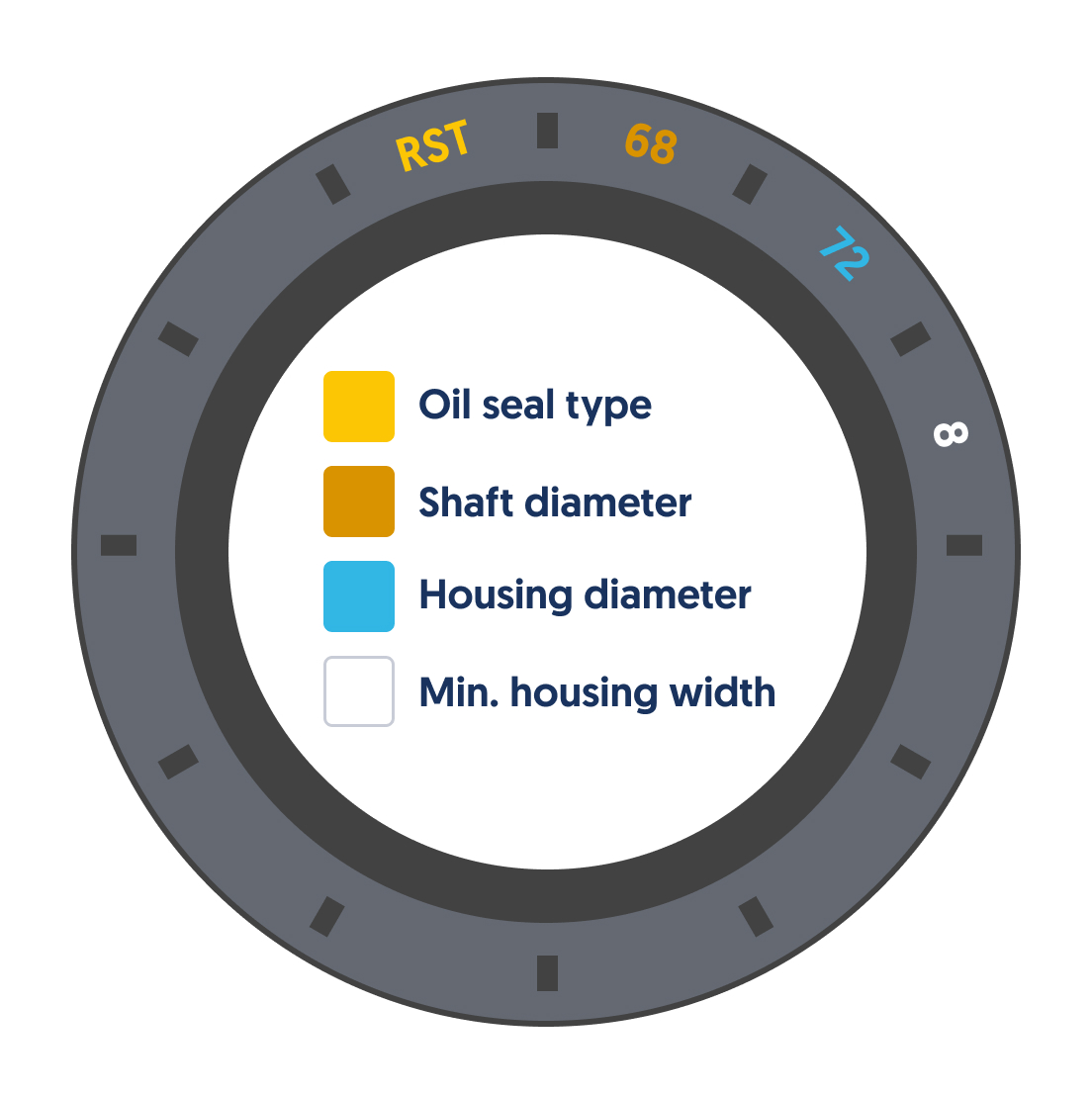
A low-profile secondary seal is a circular seal used in conjunction with a primary seal to provide extra protection against leaks in storage tanks and other containers.
These unobtrusive seals fit snugly within the gap between the primary seal and the tank opening. They are made of compressible yet durable materials like polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or nitrile rubber that can withstand high pressures and extreme temperatures.
When selecting a low-profile secondary seal, you must consider several factors:
- The seal material – Choose a material compatible with the substances stored in the tank. PTFE works well for most chemicals, while nitrile is better for hydrocarbons.
- Temperature range – The seal must withstand the full range of temperatures the contents will reach. High-performance plastics like PTFE can handle up to 500°F, while most elastomers are limited to 400°F or below.
- Chemical resistance – The seal must resist degradation and wear from exposure to the stored chemicals. PTFE is chemically inert and resistant to nearly all substances. Nitrile also offers broad chemical resistance.
- Pressure rating – The seal must be rated for the maximum pressures expected in the tank to avoid failures. Most low-profile seals can handle 50-150 PSI or higher.
By selecting a low-profile secondary seal constructed of the proper material, with appropriate temperature and chemical resistance, as well as a high enough pressure rating, you can achieve an effective barrier against leaks for your storage tank system.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Low-Profile Seal
When selecting a low-profile seal for your tank application, there are several key factors to consider:
Size and Fit
Selecting a seal that properly fits your tank opening is critical. Measure your tank opening carefully and choose a seal size that provides full coverage and an airtight fit. For irregularly shaped openings, a custom seal may need to be fabricated.
Material
The material used depends on your specific needs and operating conditions. Common options include:
- EPDM: Durable, resistant to chemicals and weathering. Suitable for most applications.
- Silicone: Flexible, temperature resistant. Good for high-heat applications.
- PTFE: Chemical resistant, non-stick. Used in corrosive environments.
- Neoprene: Resilient, resistant to oils and chemicals. Used for heavy-duty industrial sealing.
Temperature Rating
Ensure the seal material can withstand the operating temperatures of your tank application. EPDM and silicone seals typically offer the widest range.
Chemical Resistance
If your tank will contain harsh chemicals, select a seal with high chemical resistance to those specific substances to prevent degradation. PTFE and fluorocarbon seals offer the broadest chemical resistance.
Cost
Seal material, size, and customization needs directly impact cost. Compare options to determine the most affordable and cost-effective solution for your unique requirements.
In summary, analyzing your tank dimensions, operating conditions, and performance needs will enable you to choose a reliable low-profile seal tailored to your precise application. With the proper seal in place, you can have confidence in achieving an enduring, high-quality seal and avoiding unplanned downtime or product loss.
Designing Your Low-Profile Seal for Optimal Fit
To ensure an optimal fit for your low-profile secondary seal, careful design considerations must be taken into account.
Size
Choose a seal size that properly fits your tank opening for maximum effectiveness. An oversized seal will not properly secure the tank, while an undersized seal will not provide adequate coverage. Measure your tank opening and choose a seal size that matches those dimensions.
Material
Select a seal material suitable for your operating conditions. Common materials include EPDM, silicone, fluorosilicone, and PTFE. EPDM and silicone can withstand high temperatures, while PTFE is chemically resistant. Choose a material that is compatible with the substances stored in your tank.
Attachment Method
Determine how the seal will be attached and secured to your tank. Adhesive-backed seals provide an easy installation onto clean, dry surfaces. Bolt-on seals require drilling mounting holes but can handle more extreme conditions. Choose an attachment method that suits your tank design and application needs.
Gasket Profile
Consider the gasket profile that will best seal your tank. “O” ring and flange gaskets provide flexible sealing for irregular surfaces. Flat gaskets require precisely machined sealing surfaces. An optimized gasket profile mates securely with your tank opening to prevent leaks.
By carefully accounting for size, material, attachment method, and gasket profile in your low-profile secondary seal design, you can achieve an optimal fit and maximize the effectiveness of your tank seal. Precise measurement, compatibility checks, and gasket profiling will help create a tailored solution for your unique sealing requirements.
Conclusion
As you can see, selecting the proper low-profile seal for your specific application requires careful consideration of several factors. Not only must you determine the correct material based on chemical compatibility, temperature range, and durability needs, but you also need to choose a seal profile that will provide an optimal combination of compression and flexibility for your tank design. By taking the time to fully understand the requirements of your system and considering how different seal options will perform under those conditions, you can select a high-quality, long-lasting solution that will provide an excellent secondary seal and help ensure the safe, consistent performance of your tank.